Learning ggplot2
本课程介绍三种R语言的绘图工具包:plot,qplot,ggplot。三种绘图包的能够和语法均不相同。
plot命令是R语言自带的绘图命令,绘图效果简单,适宜数据分析时绘图。
qplot命令是R语言初级绘图语言包,能够提供符合出版物标准的简单绘图。得到的图形大方美观。
Lesson: Regression Models Introduction
制图:plot(jitter(child,4) ~ parent,galton)
建立回归函数:使用函数lm(linear model),例如:
regrline <- lm(child~parent, galton)
建立回归函数之后,使用abline(add straight lines to a plot)函数将回归函数在图表中画出,例如
abline(regrline, lwd = 3, col = "red")
#lwd = line width, col = line color
画出直线之后可以使用函数summary查看回归函数的各类参数包括残差, 系数,相关系数等等。
qplot
qplot is a basic function in ggplot2 package. It provides some basic plots (e.g. points, smooth, boxplot) for users to learn their database generally.
qplot(hwy, displ, data = mpg)
qplot可调的参数有许多,如下展示
qplot(x, y, data=, color=, shape=, size=, alpha=, geom=, method=, formula=, facets=, xlim=, ylim= xlab=, ylab=, main=, sub=)
x, y, data, color, shape, size这些参数很容易理解。可以使用不同的变量实现变化。
alpha用于调节透明度。0就是全透明,1就是实心。
geom用于调节图表类型,有以下几个选项”point”, “smooth”, “boxplot”, “line”, “histogram”, “density”, “bar”, “jitter”.
point表示散点图
smooth做出拟合的曲线图
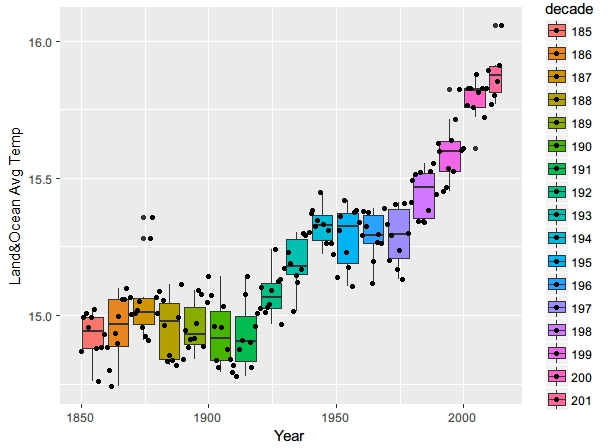
boxplot做出股价图,此处不使用自定义的最高值,最低值和平均值,而是使用fill定义group,自动计算
qplot(year,averTLO, data = gt_sum, xlab = "Year", ylab = "Land&Ocean Avg Temp", geom = c("boxplot","jitter"),fill=decade)
line做出折线图
histogram只针对单变量的柱状分布图,纵轴为count,横轴为该单变量。
density同样只针对单变量,画出该单变量的密度分布图。纵轴为density,横轴为该单变量。
bar即为常规柱状分布图,定义两个变量,利用fill变量可以实现多种变化
qplot(factor(cyl), data=mtcars, geom="bar", fill=factor(gear))

jitter则是在x轴上产生随机变量从而避免图形重叠带来的困扰。例如
p <- ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy))
p + geom_point()
不用jitter散点图的效果

p + geom_point(position = "jitter")
使用上jitter的效果
method和formula这两个选项是针对smooth这个选项而出现的。当smooth选项被调用,默认的拟合方法为loess。还有其他拟合方式允许被调用,如’lm’:线性拟合,’gam’:generalized additive models,”rlm”: robust regression
For example, to add simple linear regression lines, you'd specify geom="smooth", method="lm", formula=y~x. Changing the formula to y~poly(x,2) would produce a quadratic fit. Note that the formula uses the letters x and y, not the names of the variables.
For method="gam", be sure to load the mgcv package. For method="rml", load the MASS package.
cited from Quick-R

facets这个选项可以利用变量生成不同的分图,该选项的表达方式为:facets=rowvar~colvar,若rowvar或colvar不需要设置变量则用“.”代替。例如facets = .~colvar
利用coord_flip()可以将图表翻转
ggplot(diamonds, aes(color, fill=cut)) + geom_bar() + coord_flip()

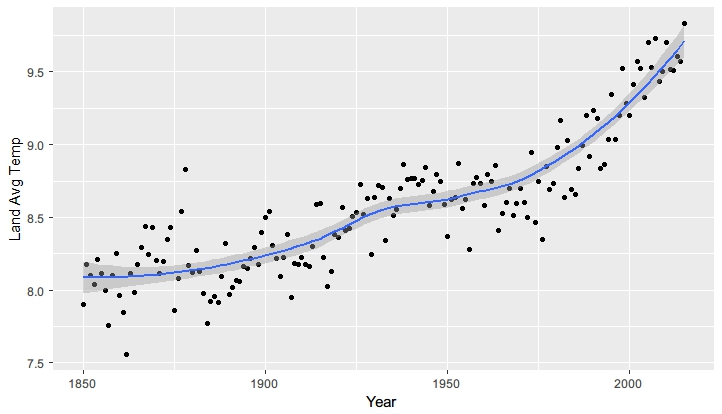
需要叠加不同类型的图表是使用c指令,e.g. c("point", "smooth")
qplot(year,averT, data = gt_sum, xlab = "Year", ylab = "Land Avg Temp", geom = c("point","smooth"))
xlim, ylim, xlab, ylab均容易理解 main,sub用于调节主副标题
ggplot2
ggplot采用图层式绘图方法,可根据自己的意图添加想要的图层,适合绘制复杂的大图。
下面是一个展示ggplot绘图语法的例子,其中mpg是ggplot自带的一个关于汽车品牌,性质的数据库。hwy和displ分别是mpg数据库中的字段,表示每加仑汽油行驶的里程数和汽车的排量。
>g<-ggplot(mpg, aes(hwy, displ))
>g+geom_points()+geom_smooth()
How to export a table. ``` write.table(dataframe, “pathway”)